Current Types
Magnetic particle inspection equipment is generally fitted with low voltage high current transformers as they reduce the risk of electrical shock to the operator.
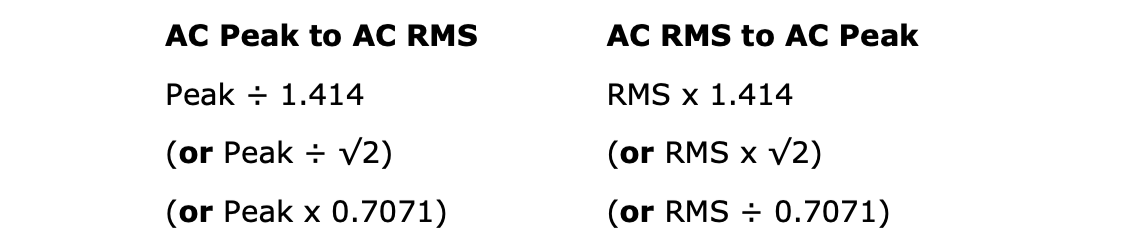
Magnetic Particle Inspection using electrical apparatus can use several types of ammeter to quantify the amount of current employed which can measure the waveform of the current in RMS, peak, mean and mag amps. Hence ammeters must show the unit/ method of measurement and normative documents, also. E.g. as to BS EN ISO 9934 which quotes all currents in amps ac RMS, whereas most American literature are in peak values.
Conversion from peak to RMS, or vice versa, is relatively simple using the following formulae:
Each waveform of the current has advantages and disadvantages.
The following waveforms/power supplies are shown as single phase power supplies, however, MT equipment will often use three phase power supplies as:
- Larger currents are available, e.g. single phase up to 3000 amps max three phase 6 – 20,000 amps
- Swinging fields are also now possible, i.e. the bench equipment is automatically changing from CF to MF and vice versa, allowing the operator to view in all directions in one operation. NB. Also referred to as sequential field of multi-directional testing.
- Longer duty cycles on the equipment.
BS EN ISO 9934: Part 3 now quotes current generators, magnetic benches and AC portable electromagnets shall have a minimum duty cycle > 10% at maximum output and the current ‘on’ time shall be > 5 seconds. Duty cycle is defined as the fraction of time that a system is in its ‘active’ state i.e. current shot time of capability 5 seconds in a 10 second period would be a duty cycle capability of 0.5 or 50% duty cycle:
t = Active Time
T = Period of function